Buster a 9 month old Springer Spaniel was attacked by a Bull Mastiff whilst out for a walk on his lead with his owner. He was rushed to our Hounslow surgery, where he was given immediate treatment for shock, and placed on a fluid infusion pump.
Buster had severe bite wounds to his head and neck. Further investigations of his wounds revealed that he had suffered a 90% laceration to his wind pipe (trachea). This was a life-threatening injury, so Buster was anaesthetised and had an airway tube passed across the torn wind-pipe to administer oxygen and anaesthetic gas, before being rushed into the operating theatre, where his torn wind-pipe was repaired, together with other skin wounds.
Buster needed close anaesthetic monitoring for this delicate surgery and required a continuous ecg (monitoring heart rate and rhythm) and blood pressure monitoring, throughout the procedure.
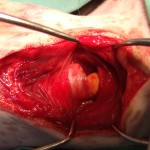
torn wind-pipe (with orange airway tube visible)
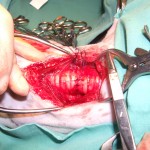
repairing wind-pipe
Buster’s breathing immediately improved, and he was kept in the hospital to monitor his recovery.

Buster recovering from surgery
Buster continued to recover well and here he is the day following surgery looking a little the worse for wear, but progressing encouragingly well. His appetite had returned which is always a good sign!

one day post surgery